What is AdBlue and what is it for? Problems with AdBlue?

AdBlue
Fuel ignition causes a sudden rise in pressure (up to 250 bar) and temperature (up to 2.500 degrees). Of course, these are models with diesel engines, since gasoline engines do not need AdBlue, that is, they have a different problem of cleaning the exhaust.
How does a diesel engine work?
The engine sucks in air at the suction stroke, whose compression pressure rises to 50 bar, and the temperature to about 550 degrees. Both compressed and hot air inject fuel that instantly evaporates and ignites, resulting in a sharp rise in pressure (up to 250 bar) and temperature (in some parts of the cylinder up to 2.500 degrees). Although these are extreme values, they usually do not damage the engine, because these are temperature values at certain places in the cylinder that decrease sharply as the piston moves downwards.
In addition to pressure and temperature as the main consequences of fuel combustion, numerous combustion products, several dozen different chemical compounds and soot particles appear. Since the fuel is a hydrocarbon, the main products of combustion are carbon compounds (CO, CO2), water vapor (H2O) and a certain amount of unburned hydrocarbons (HC). As the intake air contains 79% of nitrogen in conditions of high temperature, nitrogen and oxygen molecules combine and form very dangerous nitrogen oxides (NOx). Almost all combustion products produced in the engine cylinder, except water vapor, are toxic, carcinogenic or in some way environmentally unacceptable.

A common image with modern cars. The blue plug is for AdBlue
In 1988, the European Economic Community adopted Directive 88/77 / EEC defining the Euro 0 or Euro I standard, which for the first time defines the quantities of the most important combustion products: carbon monoxide (CO), unburned hydrocarbons (HC), nitrogen oxides (NOx) and solids (PM).
As the standards became more stringent, the interventions on the engine became more demanding, which initiated the introduction of turbines with variable geometry, ie solutions such as the return of exhaust gases (EGR) to the cylinder. However, the possibilities of achieving the required limits of harmful things only by interventions on the engine were soon exhausted, so devices for post-treatment of exhaust gases such as oxidation catalysts, particle filters and the like had to be installed. The introduction of the Euro 4 norm was one of the milestones that set (during that time) strict standards for the first time initiated the emergence of SCR technology.
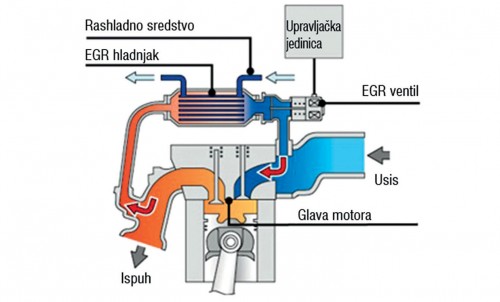
Exhaust return system displays
EGR
EGR (Exhaust Gas Recirculation) is a technology by which the exhaust gases are returned to the cylinder, where they de facto act as an inert gas, which was one of the ways to improve the exhaust gases. The reason for the return of gases lies in the fact that diesel engines must work with a constant amount of air, that is, they must have twice the amount of air that is necessary to burn all the fuel.
This leads to a situation where there are free oxygen and nitrogen molecules in the cylinder from the air, which under high temperature and pressure conditions merge to produce highly undesirable nitrogen oxides (nitrogen monoxide-NO and nitrogen dioxide-NO2) for which the common name NOx is used.
By returning the burned gases in the cylinder, part of the air is replaced with inert gas, which reduces the possibility of NOx formation, because there is less free oxygen and nitrogen. Return gases can make up to 30 percent of the volume during suction.
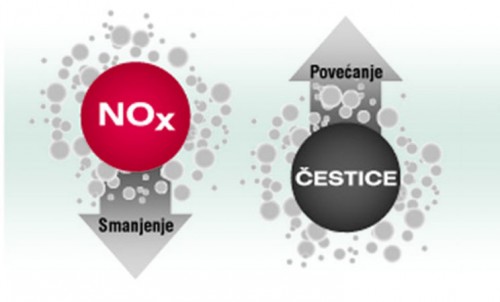
Reducing the amount of NOx increases the amount of particles, so combining multiple technologies is essential
As always in nature, one phenomenon always causes another, so although they reduce NOx, the return gases simultaneously cause another problem: not better combustion in which the peak temperatures are slightly lower, which in turn leads to an increase in the amount of solid particles.
NOx and solid particles have conflicting chemical factors, so a higher proportion of EGR in the intake means a higher amount of particles (PM), so in most cases it is necessary to install a particle filter. Also, by increasing the share of return gases, consumption increases, which is why the rest of the return never exceeds between 20 and 30 percent, because after that consumption begins to grow sharply.
SCR
Some manufacturers have only used the Euro 4 and Euro 5 standards Selective Catalytic Reduction SCR without technology EGR. It is a relatively simple but very effective solution in which a solution of urea (known as AdBlue) is injected into the exhaust, which produces ammonia that binds to NOx, producing non-hazardous nitrogen and water vapor. But such a solution, in addition to the installation of a special SCR catalyst, requires the installation of an additional AdBlue tank, which must also be replenished. Consumption of the AdBlue additive is about 5% of fuel consumption.
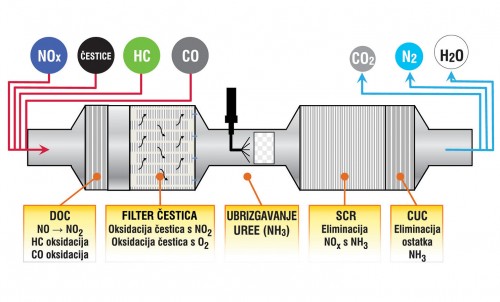
AdBlue is injected into the exhaust, producing ammonia that reacts with NOx
Given the very low amounts of harmful ingredients in the exhaust, most manufacturers have decided to combine both EGR and SCR to achieve the Euro 6 standard. So with help EGR-a reduces the amount of NOx, but an SCR catalyst must be installed to eliminate NOx completely.
Of course there is a particulate filter that regenerates regularly (usually automatically except in special driving modes) due to the slightly larger amount of particles it has EGR technology.
Some manufacturers only use SCR, which means that there are relatively few particles (but a filter is nevertheless necessary) and an SCR catalyst that uses a slightly larger amount of AdBlue in this case because it is necessary to eliminate more NOx.

AdBlue is available at gas stations in different packaging
AdBlue
AdBlue is a solution of urea in water and contains 32,5 percent urea and 67,5 percent distilled water. The composition and quality are defined by ISO 2241 or DIN 70070. The content of different metals must not exceed 0.2 mg / kg in order not to damage the SCR catalyst.
The name AUS32 (Aqueous Urea Solution 32%, or aqueous urea solution of 32%) and DEF (or Diesel Exhaust Fluid) also appear. AdBlue is relatively susceptible to temperature, so it must be stored in the right conditions to maintain the required quality (freezes to -11,5 degrees).
AdBlue - problems

The AdBlue fluid in the vehicle is filled into a special tank, which in most cars is located under the same hood as the fuel tank plug. The AdBlue cartridge cap is characterized by a blue cap. Urea is available at gas stations packed with small canisters or pumped through special filling stands.
AdBlue injection significantly reduces the harmful emissions of modern diesel engines and improves the environment, but in the future, maintenance and servicing may become a risk for used vehicles.
The proper functioning of selective catalytic reduction requires several conditions. The problem may already occur with the injector itself functioning, which can be caused by wear or overheating. The nozzle faces high exhaust gas temperatures. Damaged and poor spray injection can only be detected by factory diagnostics. Unfortunately, the moment when an injector defect is detected, it may be too late and you need to prepare for the consequences.
Due to poor spraying, unevenly injected urea can collect on the walls of the exhaust pipe where it crystallizes over time and in extreme cases clogs the exhaust gases. As a result, vehicles have a problem with meeting the prescribed exhaust emissions. There is also a dramatic decrease in performance as clogged exhausts reduce the exhaust from the engine and create back pressure. The turbocharger of a turbocharged engine brakes and high resistance to back pressure can cause its destruction.
Careless injection of urea also depends on the perfect tightness of the exhaust system, which in older cars may not always be met. If insufficient sealing of the exhaust system is provided, the urea crystallizes again. It is easier to detect this problem than an injector, because AdBlue crystallization can be seen in a quick inspection of the exhaust pipe outside, where it leaks through the opening.
Recommendation of similar texts:

Hi there, I am Mladen and I am an auto enthusiast. I started this blog years ago to help like minded people share information about latest cars, car servicing ideas, used car info, exotic cars, and auto technology. You will find helpful articles and videos on a wide variety of cars - Audi, Mercedes, Toyota, Porsche, Volvo, BMW and much more. Ping us if you have anything cool to share on latest cars or on how to make older cars more efficient, or just want to say hi!








Respect,
My NOX probe got hurt on the Peugeot 3008, the price is great, my friends advise me to adblue off the software!
I beg your opinion.
i have the same case, PUG 3008, 1.6HDI, 88KW. surfing the net I come to the conclusion that it is an inadequate plug of the urea container, which does not have a vent generiso vacuum in the system that loads the urea pump so that church. A very common problem with these engines was solved in 2017 with a new tank and plug. We unfortunates with vehicles before that correction are doomed to constant problems with this system: the pump, the hoses, and the crystallization in the exhaust. I am closest to the solution of abolishing urea and restoring the environment from EUR6 to EUR5. The only fear is the passability at the technical inspection ??
I have a Citroen C-3 in 2015, end no. chassis; VF7SCBHW6FW619073 I have a problem, my service lights up and the urea lamp burns. Where in Serbia can I remove the pump and tank, repair, clean the pump. Where do they do it in Serbia? pump and tank. Please help. THANK YOU FORWARD!
And maybe try at an authorized service center. LP
Respect, where on the Mercedes r320 2008 is poured ad blue? It won't go faster than 140km / h so I think it's up to the dpf filter. Thanks