Which Engine Oil to Choose for a Car?

Motor oil
On oil cans / packaging we usually come across two labels: API (American Petroleum Institute) and ACEA (Association des Constructeurs Europeens d'Automobiles), good / quality oils must have both specifications written on the packaging, and understanding them is very important for choosing a quality oils for either petrol or diesel engines.
API
This specification is further divided into two subcategories (for passenger vehicles) which are:
- S - for gasoline engines
- C - for diesel engines
Most of the oil packages are divided into one and the other subcategories by API, e.g. SL / CF (the first SL code is for gasoline engines, the second CF code is for diesel engines) ie. quality oils must have one and the other subcategories listed!
The age table for each API oil specification by year when it was introduced is as follows:
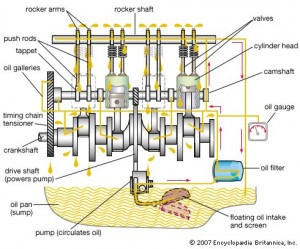
Gasoline engine scheme
- SG - Introduced in 1989, contains the additive of additives against the formation of oil sludge.
- SH - Introduced in 1993, meets the same testing standards as the earlier SG specification, but includes a maximum phosphorus content of 0.12%, also has better stability and resistance, added additives to suppress foaming and evaporation.
- SJ - Introduced in 1996, it meets the same testing standards as the SG / SH specifications, but includes a maximum phosphorus content of 0.10%, also with variations of improved additives to combat foaming and evaporation and for better oil resistance and stability.
- SL - Introduced in 2001, the specification further improved from earlier, especially suitable and tested for all new modern engines, also meets / meets all currently prescribed environmental standards.
- SM - Introduced in 11 months. 2004, includes improved oxidation resistance, additional protective additives against sludge formation and wear, also better protection and more efficient lubrication at lower temperatures and exceeds the required oil change intervals compared to older specifications…
All the earlier specifications introduced before the SL are outdated for today's modern engines, suitable for some older engines, for example, because they are subject to testing standards that have been in force for more than 10 years and do not provide the same level of protection and do not contain the same high quality additive package as the SL and SM oil specifications.
Diesel engine
DIESEL ENGINES
- CD - Introduced in 1955, meets international standards for turbo diesel engines, testing has only been conducted on a single-cylinder test engine.
- CE - Introduced in 1984, with additives to reduce oil consumption, and to thicken, wear pistons and build up deposits on pistons, testing was performed on a multi-cylinder test engine.
- CF4 - Introduced in 1990, with further improved additives to reduce oil consumption and build up of deposits on pistons, testing was conducted on a low-emission eco-test engine.
- CF - Introduced in 1994, a modernized version of the CD specification, testing was again conducted on a single-cylinder but eco-test engine with low exhaust emissions. Oil intended for direct injection diesel engines.
- CF2 - Introduced in 1994, effectively protects cylinders from buildup / buildup and wear of piston rings / links. Oil designed for two stroke diesel engines.
- CG4 - Introduced in 1994, further refined CF4 specification, improved oxidation resistance and oil stability, reduced piston wear and buildup on pistons and added anti-carbon black additives, testing was conducted on a test engine powered by low sulfur diesel.
- CH4 - Introduced in 1998, a refined CG4 specification, contains additional anti-soot enhancements, further reduced piston wear and piston deposition, includes much more extensive testing on a test engine powered by low and high sulfur diesel.
- CI4 - Introduced in 2002, developed to meet environmental standards in 2004. , especially suitable for diesel engines with EGR (exhaust gas recirculation) systems and for diesel engines powered by diesel fuel with a sulfur content of up to 0.5%. It can also be used in engines where API CD, CE, CF4, CG4 and CH4 oils are specified.
All previous specifications introduced before CH4 are obsolete for today's modern engines, they are suitable for some older engines, because they are subject to testing standards that were valid for more than 10 years and do not provide the same level of protection and do not contain such a quality package of additional additives as CH4 & CI4 oil specifications. It is especially desirable to use oils of specifications - SL, SM, CH4, CI4.

SAE 5W-30 Engine Oil
ACEA
This is the European equivalent of the American API oil specification, which further complements the description of the efficiency of a particular type of oil and the classification of oils for use in certain types of engines. It is also divided into subcategories, in this case into three subcategories, which are:
- A - for gasoline engines
- B - for diesel engines
- C - for catalytic converter or low exhaust gas engines (SAPS - sulfur ash, phosphorus, sulfur)
The table of oil specifications according to ACEA, unlike the API specification, does not refer to years, ie. years when the tests of a particular specification and the description of improvements were introduced, it already refers to the description of efficiency and classification of oils for use in certain types of engines, and it follows as follows:
- A1- For reduced fuel consumption
- A2- Standard degree of motor protection and efficiency (currently obsolete)
- A3- High engine protection and efficiency and extended change intervals
- A4- Degree reserved for the future for some direct fuel injection engines
- A5- Combination of A1 and A3 specifications by degree of efficiency and
- B1- For reduced fuel consumption
- B2- Standard degree of motor protection and efficiency (currently obsolete)
- B3- High engine protection and efficiency, and extended replacement intervals
- B4 -For diesel engines with direct fuel injection
- B5- Combination of B1 and B3 / B4 specifications by degree of efficiency
- C1-04 -For gasoline and light diesel engines, based on A5 / B5-04 specifications, low proportion of SAPS, compatible for two-way benz. or diesel catalysts.
- C2-04 -For petrol and light diesel engines, based on the A5 / B5-04 specifications, a standardized SAPS ratio, compatible for two-way benz. or diesel catalysts.
- C3-04 - For petrol and light diesel engines, based on the A5 / B5-04 specifications, a standardized SAPS ratio, compatible for two-way benz. or diesel catalysts. , high degree of protection and resistance.
Particularly desirable to use oils of specifications - A3 / B3, A5 / B5 and C3
It is desirable to choose the gradation and type of oil according to the factory specifications for a particular vehicle, ie. built-in engine model. Note, according to the type, oils are distinguished as:
- Mineral
- Semi-synthetic
- Synthetic (which includes new special oils based on "Esther" ..)
Mineral oils
Mineral oils are no longer used as such for modern engines, but exclusively for older vehicle models because they do not provide sufficient protection of the engine against wear and tear, and do not have a high quality package of additional additives.
Semi-synthetic oils
Semi-synthetic oils are, by composition, a mixture of mineral oil as a base and additional synthetic oil or VI polymer enhancer (unfortunately, mostly in the ratio of 80% of mineral 20% of synthetic base or even less for a synthetic base, depending on the manufacturer) are more affordable than synthetic but do not have such a high temperature and oxidation resistance, do not last as long as synthetic ones and require more frequent replacement intervals.
Synthetic oils
Synthetic oils are by far the highest quality choice, differing from mineral and semi-synthetic oils by spec. The processing process is characterized by excellent resistance to extremely low and high temperatures and protection of the motor against wear.
It is especially advisable to use synthetic oils with a turbo engine if the vehicle is used for short distances of less than 15 min. driving multiple times a day and in conditions where the vehicle is exposed to constant low temperatures below 5C as well as high temperatures (especially if the engine itself is mechanically modified) for which there is a special index 50 or 60 when selecting the oil, which is the upper point of oil resistance high temperatures. Synthetic oils also have better oxidation resistance as opposed to mineral and semi-synthetic ones so that, theoretically, they do not require frequent replacement intervals. These oils are generally the most expensive.
- Mineral oils are in the grading rule: 20W-40, 15W-40, 10W-40
- Semi-synthetic: 15W-40, 10W-40
- Synthetic: 5W-40, 0W-40, 5W-30, 0W-30
Specially formulated synthetic oils
Another category, which includes specially formulated synthetic oils for extreme conditions, intended primarily for modified engines with a special additive package, predominantly for use in racing / modified engines, most commonly grades: 5W-50, * 10W-60 * that certain types of these oils are not suitable for all passenger vehicles as they contain a special package of additives that are not suitable for use in everyday vehicles under normal driving / straining conditions and replacement intervals.
The recommended viscosity of the oil according to ambient temperature is as follows:
- 0 to 30C -> 20W-40 (mineral) 15W-40 (semi-synthetic) or 5W-50, 0W-40 (synthetic)
- -8 to 30C -> 15W-40 , 10W-40 (semi-synthetic) or 5W-40, 0W-40 (synthetic)
- -18 to 15C -> 10W-40 (semi-synthetic) or 0W-30 (synthetic)
- -18 to 3 -> 10W-30 (semi-synthetic) or 0W-30, 5W-30 (synthetic)

Engine oil change
Engine Oil Replacement
And finally a few words about how to do the oil change on your car at home. You need the following for this job:
- Oil Crankcase Latch Wrench (For most older vehicles, you only need a set of socket or plain combination wrenches / fork keys, while for some newer models, there are special square nuts, but you can still buy them today at a better tool shop or spare parts store. .)
- Oil filter release wrench (also available in tool shops, major malls or spare parts stores) Hand crane and three-leg washer, Waste oil drain pan of suitable volume (4 to 5l)
- Disposable PVC gloves and old waste oil wipes
Be sure to warm the engine to operating temperature before draining the oil from the system , then park the vehicle on a flat surface , apply the parking brake and engage first gear, place the jack in a position on the vehicle sill and raise the vehicle as far as it will go under the vehicle to loosen the drain plug on the crankcase and place the waste oil container in place. cranes place a three-legged pad
It is also advisable to place a spare wheel or something similar under the vehicle in case the vehicle slips off the mat or crane, which can result in serious injuries, so take special care that the vehicle is stable when performing any type of repairs on the lower part of the vehicle…
When loosening the drain plug, pay attention to the release direction because on some vehicle models it is released on the reverse side - with the standard thread that applies to most vehicles, the screw is released counterclockwise, while on certain models it is released clockwise, which we call "Counter thread", the force of the screw clamp is moderate, so if you can't loosen the screw by turning it to one side, don't force it, but try the opposite…
When loosening the bolt, immediately place the waste oil drain pan so that the center of the pan is approximately around the center of the drain bolt (pull on the PVC gloves), loosen the bolt halfway and remove the tool and continue loosening the bolt with your fingers, pushing the bolt upwards. when you release it to the end of the thread, you can suddenly pull your hand away by holding the drain screw to the side so that you will not get burned oil that will be quite hot, so be careful not to burn yourself!
Now it's time to take a break, wait a minute. 15min to drain the oil completely from the system, during which time you can release the oil filter, the oil filter is located on the front or rear of the engine block and is screwed into the engine block housing, to release the oil filter you will need the above key wrap around the filter itself (chain or belt depending on the key model) tighten the chain pass the end of the chain through the slot of the oil key and turn the key counterclockwise, if the oil filter key chain slides on the oil filter and does not move - tighten / tighten the chain try again…
Grasp the released oil filter by hand, put an old cloth under the filter and release it to the end of the thread by hand and when you remove it, turn it upside down so that the oil does not leak on the engine, because there will probably be about 2dl of oil in the filter…
When you have removed the oil filter, and when the oil has completely drained from the system, make sure to store the oil filter and old waste oil in the appropriate places, unless there are specs in your area. municipal waste bins or waste disposal centers and oil filters pour the oil into a suitable container / container and deliver it to an auto mechanic shop as the mechanics have spec.
waste oil storage and delivery containers…
Do not neglect this waste oil disposal procedure and do not discharge it into the environment or sewage system, as only one drop of waste oil can pollute thousands of liters of water !!!
Since you have selected the right engine oil for your vehicle (according to the specifications above and by grade for your vehicle model) an extremely important detail is the choice of a quality oil filter, the original oil filter filters purchased at an authorized service center are generally of the highest quality but also more expensive than the oil filters you can buy in the spare parts shops, but they are definitely worth the money, if you still decide to have a replacement oil filter stick to the renowned brands: Fram, Man , Purflux, Motaquip.
To fill the system with oil, proceed as follows - wipe the crankcase drain plug with a dry cloth, install a new copper seal ring on the drain plug (you can buy a sealing ring at any spare parts shop according to the pattern), screw the drain plug into the crankcase and moderately tighten with a wrench (with a feel, by no means tighten more than necessary!) lower the vehicle back to the ground and prepare the oil filter for mounting, here it is important to grease the oil filter gasket contact with oil before mounting back onto the engine block, dip your index finger into the oil and grease the entire surface of the oil filter rubber gasket in circular motion, thoroughly wipe the oil filter on the engine block with a dry cloth and screw the oil filter onto the block, tighten by 2/3 to 3/4 turns, and if necessary, if subsequently notice a leakage around the filter, additionally tighten with the oil filter wrench (again, with feel , do not weigh more than necessary!).
It is also a good practice to fill the oil filter with oil at least half before mounting, but it is not required. After mounting and tightening the exhaust screw and oil filter, lowering the vehicle to the ground, you can begin filling the system with oil.
Unscrew the oil filler cap at the top of the engine on the valve cover and slowly pour the oil into the system. The usual oil volume for automotive engines varies from 3.5 to 5l oil (calculated with oil filter), you can check the correct data for your vehicle in the vehicle maintenance instructions indicating the oil volume and the proper oil graduation for the engine installed in your vehicle.
When refueling, periodically check the level of the oil level control bar to avoid overfilling the system, which is as harmful as driving at low oil level!
Oil level control
Keep the ideal engine oil level between min. and maxi. markings on the control bar. When you have charged the system and read from the control bar that the level is between min. and maxi. marks, replace the oil filler cap and start the engine briefly and let it run for about 1 / 2min. to raise the oil pressure and circulate the oil through the system, turn off the engine later and check the oil level again (usually you will have to add an additional 0.5l of oil) also check the areas around the drain plug on the crankcase and the area around the oil filter for leaks, if notice a leak, tighten the bolt / filter 1/4 turn and restart the engine and check until the system is completely sealed. Try to change the oil on your vehicle regularly because old oil does a lot more damage to the engine than mileage! Use quality motor oils and the highest quality oil filters you can buy.
Retrieved from: uputstva.org
Recommendation of similar texts:

Hi there, I am Mladen and I am an auto enthusiast. I started this blog years ago to help like minded people share information about latest cars, car servicing ideas, used car info, exotic cars, and auto technology. You will find helpful articles and videos on a wide variety of cars - Audi, Mercedes, Toyota, Porsche, Volvo, BMW and much more. Ping us if you have anything cool to share on latest cars or on how to make older cars more efficient, or just want to say hi!









Great. And I've learned too much here about motor oil, every bit of it.