Capacitors
A combination of capacitors and battery formulas for the future?
Today's vehicles are mostly powered by fossil fuels or batteries and at moderate load are quite efficient, however, when suddenly high power is needed, efficiency drops and life spans become shorter
Compared to lithium-ion batteries, supercapacitors are distinguished by three features: the ability to discharge very quickly, the very long life span (about one million cycles) and the good low-temperature characteristics. The disadvantage is the inability to store large amounts of energy. To summarize, capacitors can deliver great power over short periods of time and at various temperatures, but the need to store more energy is addressed by batteries. Another of the current disadvantages of capacitors are dimensions, since the amount of energy that can be stored in capacitors is about 20 times smaller than that that can be stored in batteries, if the dimensions and mass are equivalent. Capacitors, on the other hand, can be attributed to a higher degree of safety, and with batteries can lead to breakdowns that can end up as shock news (a recent plane crash due to lithium-ion battery problems).
The long service life is made possible by the very nature of the charging and discharging processes where energy is stored in a field between two layers of conductors, while batteries store energy through chemical processes, which over time leads to a permanent loss of properties. Also, supercapacitors also perform great at temperatures of -40 ° C, when the batteries on the market today have a major problem with capacity reduction.
Vehicle supercapacitors began to be used around 2002, however the technology was expensive and has not been widely adopted. However, today we can talk about multiple price drops and increasing use. The number of elements has also been reduced by about 3 times, and hence the complexity.
Today, the supercapacitor market is "difficult" at about $ 366 million (but not just for use in the auto industry), but expected growth is about 20% year over year. By 2018, the heavy-truck supercapacitor market will reach $ 323 million, while in the passenger sector predictions are handled with a sum of $ 152 million.
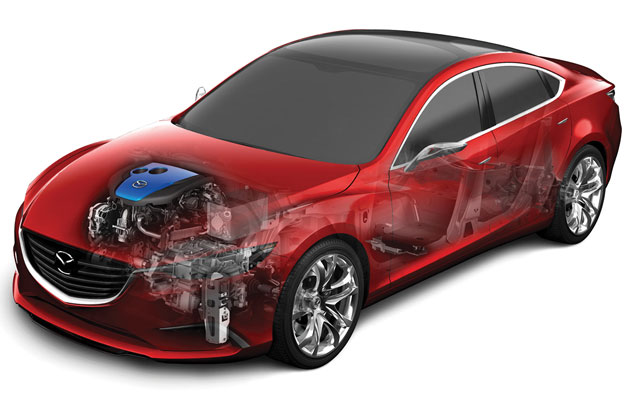
Supercapacitors in cars
One of the first applications of supercapacitors in the auto industry happened in Honda cars. Inside the house, the developed supercapacitor was used on a 2002 FCX fuel cell driven model, and the condenser was used when there was a sudden need for more power, when climbing or overtaking. In series, supercapacitors are also found in e-Hdi hybrid models of PSA concern on the second generation of start-stop systems and in Mazda's hybrids with i-ELOOP systems. There are currently about half a million cars on the roads with supercapacitors from only one manufacturer. To date, supercapacitors have proven to be very reliable and are used most when starting engines with start-stop systems that are becoming a part of everyday life. For these applications, the supercapacitor characteristics themselves are ideal.
In particular, Continental's (supplier) solution uses two regularly connected 5V volt capacitors and the capacitor helps stabilize the car's electrical grid when starting the engine. When starting with supercapacitors, the voltage in the system remains well above 10 V, while in conventional systems it drops to a value of about 8 V, which can cause malfunction of many computers.
Application in buses
Currently, most supercapacitor funding is spent on bus transportation. Thus, 10.000 diesel hybrid buses in China have supercapacitors. Each bus is equipped with about 300 supercapacitors worth $ 15.000. However, the main reason for such widespread application was government subsidies, because only because of hybrid systems implemented in this way, bus prices would be twice as high. It should be noted that after the end of government subsidies and orders for capacitors decreased dramatically.
These systems use capacitors connected to provide voltages from 400 to 700 V. When the bus is braking, the energy stored in the capacitors is released. The same energy is used to accelerate the bus to 15-20 km / h when the diesel engine is started. This avoids adverse engine operation in adverse conditions and reduces pollution, which is of paramount importance to overpopulated Chinese cities. Basically, either the condenser or the battery hybrid system is implemented on the buses. The advantage of the condenser system is the ability to quickly store and discharge energy, ideal for energy recovery when braking. Battery systems, in turn, allow more energy to be stored, for example, allowing air conditioning to operate even when the diesel engine is stationary. But as said, the batteries are heavy and are heavily influenced by the climate, so there is a dilemma when choosing which of these two systems.
What is expected in the future is a fall in prices for both batteries and capacitors and a synergistic approach to both solutions.
Text: Vanja Dragosavljevic
Retrieved from: www.vrelegume.rs
Recommendation of similar texts:

Hi there, I am Mladen and I am an auto enthusiast. I started this blog years ago to help like minded people share information about latest cars, car servicing ideas, used car info, exotic cars, and auto technology. You will find helpful articles and videos on a wide variety of cars - Audi, Mercedes, Toyota, Porsche, Volvo, BMW and much more. Ping us if you have anything cool to share on latest cars or on how to make older cars more efficient, or just want to say hi!