Bosch VP44 high pressure pump - Bosch VP44

Bosch VP44
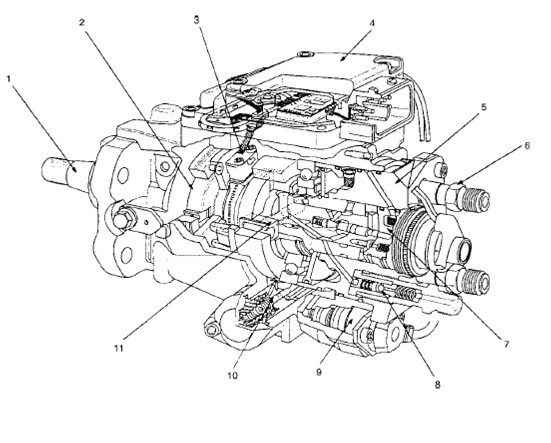
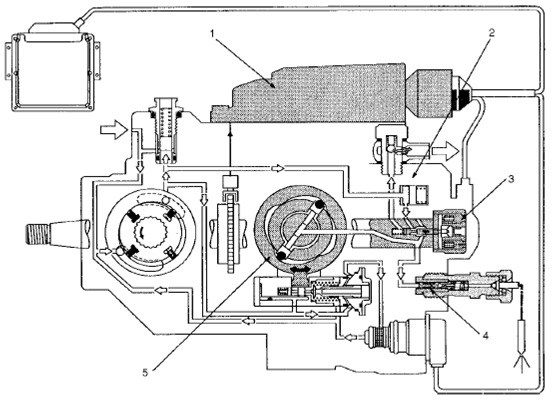
Composition Bosch VP44 High Pressure Pumps:
1. Shaft
2. Power supply (rotary pump)
3. Axle speed sensor
4. ECU pumps (PSG) - PSG = Pumpen Steuer Great (German)
5. Distributor heads
6. Constant Pressure Valve (CPV) Holder Housing Pressure Relief Valve Housing
7. High pressure solenoid valve
8. Constant Pressure Valve (CPV) - permeable relief valve
9. Injection angle control valve
10. Timer - adjust the injection angle
11. High pressure pump radial piston
Instead of old axial pumps, radial pump distributors use a camshaft to allow fuel injection at high pressures. This pump has been developed to provide the most appropriate amount of fuel injection and timing (angle, time) of injection to satisfy engine reliability, low smoke, low noise, high engine power and cleaner exhaust.


Bosch VP44 High Pressure Radial Distributor Pump is capable of producing 1000 bar pressures.
High fuel injection pressure, the fuel is sprayed at high pressure with a high degree of penetrating power (fuel droplets penetrate further) and with greater dispersion and distribution (mixing with air is improved) and results in better combustion. This contributes to cleaner exhaust emissions.
Quick control of the amount of fuel for injection and injection time is performed by control units, which enables lower fuel consumption and high power output. As a control unit the system consists of a motor control module - ECU - (ECM) and a pump control unit -ECU pump- (PSG).
When the amount of fuel injected increases, to increase engine power at acceleration, the excess fuel usually smoke. The Bosch VP44 fuel pump, precisely controls the amount of fuel injection, even in this range prevents smoke that is negatively affected by acceleration.
Bosch VP44 - Low fuel pressure circuit
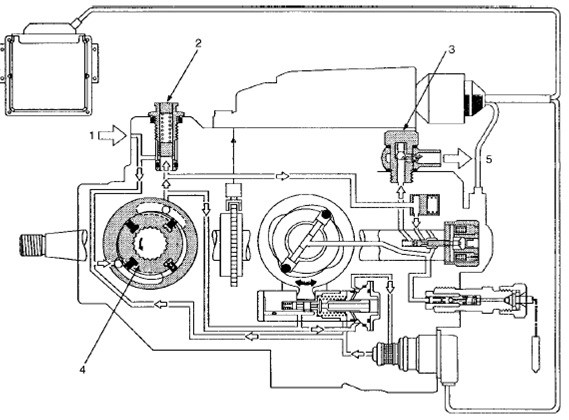
Parts of construction:
1. Fuel Input
2. Control valve
3. Check valve
4. Power pump
5. Return to the fuel tank
The low fuel pressure circuit must provide sufficient fuel for the high pressure fuel circuit.
Feed pump - Bosch VP44
The feed pump is driven by a drive shaft, sucks in fuel and supplies fuel to the high pressure pump. The wings are in the rotor, pressed against the inner annular housing and centrifugal force of rotation by spring force during the formation of the chamber.
When the blades rotate, the circumference of the blades increases when in the recessed portion of the annular housing connected to the inlet, the pressure is low. As the wings rotate, the bumps pass, the wing volume decreases and the fuel pressure increases. At the outlet, the volume of the wings is smallest and the pressure is greatest, from there the fuel goes to the control valve and to the high pressure pump.
Control valve - Bosch VP44
When the feed pump increases the speed, then the delivery pressure of the fuel supplied from the feed pump exceeds the spring force of the control valve and the piston moves upwards. Excess fuel flows through the vent and returns to the inlet, and delivery pressure is maintained to a certain extent.
When the feed pump speed decreases and the delivery pressure decreases, the spring pushes the piston down and closes the passage.
Overflow valve - Bosch VP44
When the pressure of the fuel returned from the distributor head exceeds the spring force, the overflow valve ball goes up. Excess fuel passes through the opening and returns to the fuel tank and the pressure inside the pump does not exceed a certain pressure.
Bosch VP44 - High fuel pressure circuit
Parts of construction:
1. ECU pumps (PSG)
2. Distributor heads
3. High pressure solenoid valve
4. Constant Pressure Valve (CPV)
5. High pressure radial pump
High pressure pump radial piston
The radial piston performs rotational motion, the inner bank makes piston motions to suck and compress the fuel in the piston chamber.
1. Fuel suction
When the piston radial rotates, the piston moves from the upper dead position, the circumference of the piston chamber increases. The piston chamber is filled with fuel as a result of the internal pressure of the pump. During this period, the high pressure solenoid valve is open. And the high pressure passage of the feed pump is open.
2. Fuel compaction
When the radial piston rotates, moves, from the lower dead point, it is pressed against the edge of the ring so that the circumference of the piston chamber decreases and the fuel compresses until the pistons reach the upper dead point. During fuel injection, the high pressure solenoid valve needle valve is in the seat, closed. And the high pressure passage of the feed pump is closed.
Distributor heads
The distributor head distributes high pressure fuel, which flows through the rotating rotor shaft, distributes slots and high pressure pipes in (4 cylinders: 4) to the cylinder engine via a constant pressure (CPV) valve and a nozzle.
The needle of the high pressure solenoid valve changes the passage to the high pressure radial piston of the fuel pump between the suction and the fuel compression.
High pressure solenoid valve
The high pressure solenoid valve has a valve needle, which opens and closes with a command from the ECU pump (PSG). The consequence is the opening and closing of the fuel injection controls.
Constant Pressure Valve (CPV) Thrust Relief Valve
A constant pressure (CPV) valve reduces the return pressure (rebound wave) generated on the nozzle valve when the nozzle closes, to prevent the nozzle from reopening (secondary injection). Also, a constant pressure valve (CPV) suppresses cavitation in high pressure pipes, which is the cause of pipe erosion, and maintains a stable pressure in the injection pipe (residual pressure) to provide stabilized injection timing for later.
Bosch VP44 - Timing control - Injection angle control
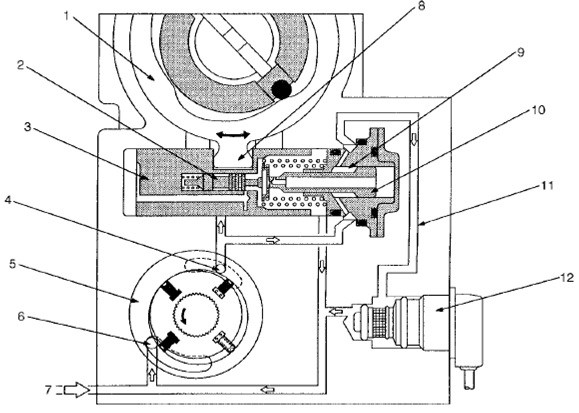
1. Camshaft
2. Servo valve
3. Clip timer
4. Exit
5. Power pump
6. Entrance
7. Fuel Input
8. Pine
9. Ring Chamber - Circular Chamber
10. Hydraulic plug
11. Returns
12. Timing Control Valve (TCV) - injection angle control valve
The timing device determines the optimum injection time from variations in engine speed. The fuel pressure of the supply from the feed pump is adjusted according to the speed depending on the regulation of the valve. This delivery pressure acts on the annular chamber with a hydraulic plug as a control pressure.
The pressure chamber in the annular chamber controls the opening time of the injection angle control valve (TCV). The timing piston is connected to the pin of the cam ring. The shifting timing piston is transferred to the camshaft in the form of rotary motion. Turning the right timing piston (in the spring section) earlier injection time.
Injection Angle Control Valve Operation - TIMING CONTROL VALVE (TCV)
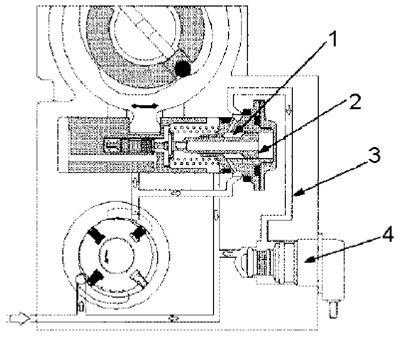
1. The ring chamber
2. Hydraulic plug
3. Return spring
4. Timing Control Valve (TCV) - injection angle control valve
Injection Angle Control Valve (TCV) acts as a throttle, using the quick opening and closing (cycles) of the Injection Angle Control Valve (TCV) needle.
In normal operation, the TCV controls the pressure acting on the annular chamber so that the hydraulic plug of the cam moves to any position, from position back to position forward. The valve is controlled by the pump ECU (PSG).
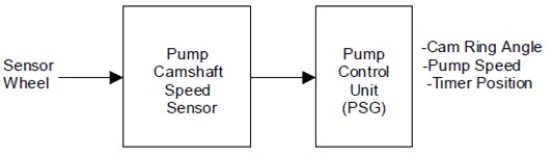
Pump Shaft Speed Sensor - PUMP CAMSHAFT SPEED SENSOR
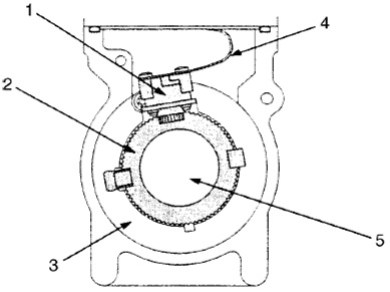
1. Pump shaft speed sensor
2. Sensor wheel
3. Pump shaft speed sensor support ring
4. Flexible conduit connector
5. Drive shaft
When the shaft rotates, the pump shaft speed sensor takes the form of a wheel sensor signal and an electrical pulse is sent via a flexible conductor to the pump ECU (PSG). From these signals, the ECU of the pump (PSG) can determine the average pump speed and the current pump speed.
The pump shaft speed sensor is mounted on the camshaft. Thus, the relationship between the camshaft and the pump shaft speed sensor signal is constant.
The pump shaft speed sensor signal is used for the following purposes:
To determine the current angular position of the cam ring
To calculate the actual speed of the fuel injection pump
To determine the actual position of the piston timing.
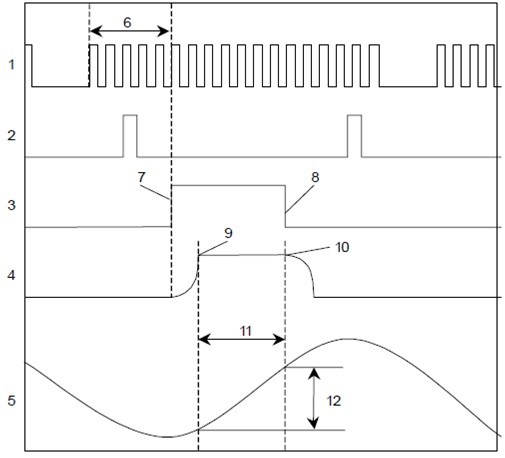
1. Pump shaft sensor signal
2. Crankshaft position sensor signal
3. High-pressure solenoid valve control pulse
4. Moving the high pressure needle valve solenoid
5. Camshaft (cam profile)
6. Impulse counter
7. High pressure solenoid valve closed
8. High pressure solenoid valve open
9. Start delivering pressure
10. End of pressure delivery
11. Pressure delivery angle
11. Effective impact
1. The current angular position of the cam ring
The current camshaft angular position goes to the ECU of the pump (PSG) and the ECU of the camshaft controls it via the signal control of the high-pressure high-solenoid valve.
The current angular position changes according to operating conditions, the high pressure solenoid valve opens and closes at intervals that allow the camshaft to be positioned correctly.
2. Actual pump speed
When the crankshaft speed sensor is faulty, the ECU of the engine (ECM) uses the pump speed suggesting a replacement signal.
3. Current position of the taiming piston
The actual position of the taming piston can be determined by comparing the crankshaft speed sensor signal with the pump axis angle sensor. This position is used to control the injection angle.
ECU pumps - PUMP CONTROL UNIT (PSG)
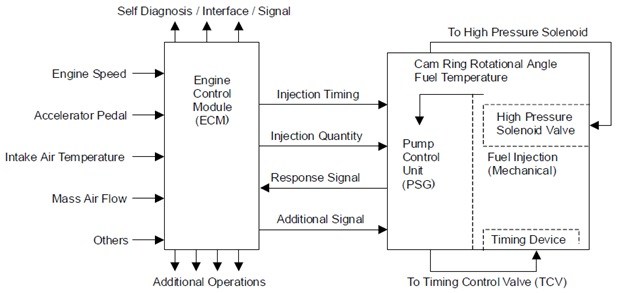
The radial piston pump distributor uses two control modules to fully control the engine management system.
Engine Control Module - ECU, motors (ECM)
Pump Control Unit (PSG) = Pumpen Steuer Great (German)
The pump control unit (PSG) receives signals from the sensor for determining the pump camshaft angle, pump speed and fuel temperature.
This value is then compared to the desired value sent by the engine control module (ECM) such as the desired injection time and the desired amount of injection fuel.
The Engine Control Module (ECM) processes all engine process data and environmental data obtained from external sensors to make the necessary engine adjustments.
The maps for both control units are coded. For control units, input processes with sensor data. The microprocessor then determines the operating conditions and calculates the adjustment values for optimal operation.
Data exchange between the ECM and the pump control unit (PSG) is defined via the CAN-BUS system.
List of cars with pump VP44:
- Audi A4 / A6 / A8 2.5 TDI V6
- BMW (E46) 320D / (E39) 520D
- Ford Fiesta / Focus / Transit / Monde
- Nissan Almera / Patrol / Terrano
- Rover 25/45
- SAAB 9-3 / 9-5
- Škoda Superb 2.5 TDI V6
- Suzuki Grand Vitara 2.0D
- Opel - Vauxhall Astra / Combo / Corsa / Frontera / Meriva / Omega / Signum / Vectra / Zafira
- VW Passat 2.5 TDI V6
Used literature of the company "ISUZU MOTORS LIMITED"
Recommendation of similar texts:

Hi there, I am Mladen and I am an auto enthusiast. I started this blog years ago to help like minded people share information about latest cars, car servicing ideas, used car info, exotic cars, and auto technology. You will find helpful articles and videos on a wide variety of cars - Audi, Mercedes, Toyota, Porsche, Volvo, BMW and much more. Ping us if you have anything cool to share on latest cars or on how to make older cars more efficient, or just want to say hi!








Where can I buy a new SPEED SENSOR SPEED PUMP SHAFT
FOR OPEL ZAFIRU 2003 2.0 DIESEL
FOR BOS PUMP WITH 2 JACKS
I have a problem nisan terano ll 3 tdi hardly starts after overhauling the high pressure pump.
what could be done here
Hello, I have a question related to the High Pressure Pump Module, namely I have a problem with the ford transit 2.4tddi. I'm interested because I can't find the same one with the same transit markings, would it match the Audi 2.5 163 hp because I found an identical module with the same numbers that is from the mentioned car, thank you in advance